Contents
In this article we will look at:
- What is diabetes mellitus type1?
- How does diabetes type 1 occur?
- Who is prone to diabetes type 1?
- Symptoms of diabetes type 1
- Diagnosis of diabetes type 1
- Complications of diabetes type 1
- Treatment for diabetes type 1
You can click on any of the links above to navigate to the section of your interest.
What is diabetes mellitus type 1?
Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 is the most severe form of diabetes, in which not enough insulin is produced by the body. The lack of insulin results in high blood sugar levels.
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that allows your body to use glucose (a type of sugar found in many carbohydrates) for energy. Insulin also helps to balance your blood glucose or blood sugar levels, by preventing it from getting too high (hyperglycemia) or too low (hypoglycemia).
Following are the normal and diabetic blood sugar levels:
Plasma Glucose Test | Normal | Pre-Diabetes | Diabetes |
Random | Below 11.1 mmol/l Below 200 mg/dl | N/A | More than 11.1mmol/l More than 200 mg/dl |
Fasting | Below 6.1 mmol/l Below 108 mg/dl | 6.1 to 6.9 mmol/l 108 to 125 mg/dl | More than 7.0 mmol/l More than 126 mg/dl |
2 Hour Post-Prandial | Below 7.8 mmol/l Below 140 mg/dl | 7.8 to 11.0 mmol/l 140 to 199 mg/dl | More than 11.1mmol/l More than 200 mg/dl |
Please Note: If your glucose levels are below 50 mg/dL or above 200 mg/dL you need to be admitted to the emergency room without delay.
How does diabetes type 1 occur?
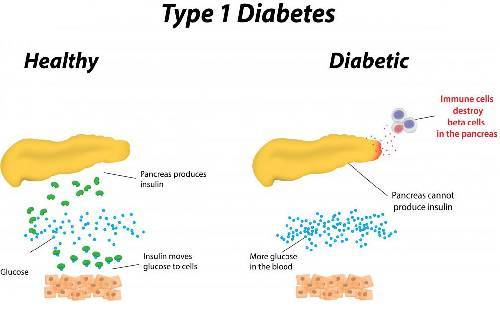
The exact cause of type 1 diabetes is unknown. Medical experts agree on the fact that this is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system of the body is mistakenly conditioned to attack and destroy the cells in the pancreas, which produces the hormone insulin.
Insulin helps to unlock the cells of the body to allow the sugar (glucose) to enter them so that the glucose is transformed into energy. If there is more sugar in the body than is required, the insulin helps to store the sugar in the liver and releases it when the blood sugar level is low, or when the body needs more sugar, such as in between meals or during vigorous physical activity. Therefore, insulin helps to balance out the blood sugar level and keep it in a normal range. As blood sugar level increases, the pancreas secrete more insulin.
If your body does not produce enough insulin or the cells in your body are resistant to the effects of insulin, you may develop hyperglycemia (high blood sugar). If the blood sugar levels stay elevated for long periods of time it can lead to long-term complications.
In diabetes type 1, insulin does not get produced in the body. Without insulin, the cells are starved of energy, and the sugar levels keep rising in the blood.
Who is prone to diabetes type 1?
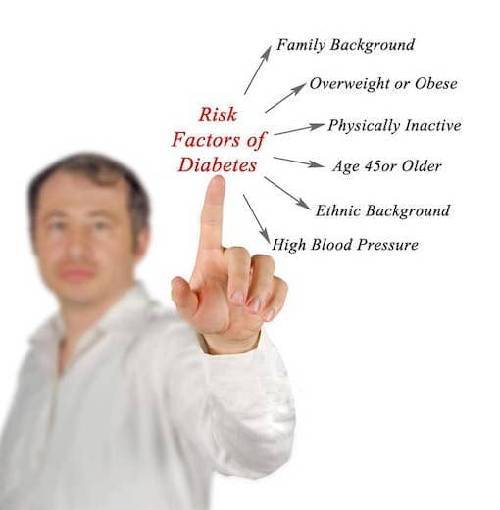
People can be prone to diabetes mellitus type 1 due to :
- Viral Infections: such as German measles, coxsackie, and mumps, which can prompt the immune system to turn against the body instead of fighting for it.
- Ethnicity: Some ethnicities have a higher incidence of diabetes mellitus type 1
- Family History: If anyone in your family has type 1 diabetes, you are at an increased risk of developing it.
- Cold Weather: It has been observed that there are more occurrences of type 1 diabetes among people living in colder climates.
- Childhood Diet: It has been observed that children who were breastfed were less likely to develop type 1 diabetes. On the contrary, children who were given cow’s milk at an early age have a higher risk of developing type 1 diabetes.
What are the symptoms of diabetes mellitus type 1? How is diabetes type 1 diagnosed?

Symptoms of high blood sugar or Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 include:
- Excessive urination
- Excessive thirst
- Sudden weight loss
- Fatigue
- Increased hunger
- Blurry vision
- Slow healing wounds
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of diabetes type 1 usually includes one or more blood tests:
- The doctor will advise you to undergo a Glycated haemoglobin (A1C) test. This test indicates your blood sugar levels for the past two to three months.This test measures the percentage of haemoglobin — an oxygen-transporting protein in red blood cells — to which the blood sugar is attached. A high percentage of haemoglobin (6.5 % or higher) indicates diabetes.
- After the Glycated haemoglobin (A1C) test the doctor will ask you to undergo an autoantibody test, which checks for antibodies that attack the pancreatic cells.
The doctor may also ask you to undergo a Random Blood Sugar Test, Fasting Blood Sugar Test and an Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT).
What are the complications of diabetes type 1?
If not managed properly, diabetes type 1 can lead to some serious complications such as:
- Hypoglycemia or Low Blood Sugar - Low blood sugar develops when you take more than the required dosage of insulin.
- Microvascular Complications - Damage to both tiny and large blood vessels due to uncontrolled blood glucose which may lead to eye, kidney or nerve diseases.
- Macrovascular Complications - Plaque build up in the in the arteries leading to possible heart attack or stroke.
What is the treatment for diabetes type 1?

Medical Treatment
The medical treatment for diabetes type 1 includes taking insulin either through injections or through insulin pumps. Additional medicines may be prescribed by the doctor to keep your blood pressure and cholesterol under control. Regularly checking your blood sugar levels is necessary.
Please consult a general physician, diabetologist or an endocrinologist if you suspect that you suffer from symptoms of diabetes.
Exercise
Physical activity is important for you regardless of the fact that you suffer from Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 or Diabetes Mellitus Type 2.
It is advisable to consult with your doctor to find out which forms of exercises suit you the best.
If you have Diabetes Type 1 you need to monitor your blood sugar before, during and after exercising. You may experience a drop in your blood glucose after exercising and therefore it is important to take precautions.
For example, you may need to take a lower dose of insulin and increase your carbohydrate intake before exercising.
Warning: To avoid any serious risk to your health please consult your doctor before starting a new exercise regimen. You may need to change your diet, and the dosage of insulin, or of other medicines before you start exercising.
Patient Experiences




Questions answered by trusted doctors



Related videos
Related articles
Multiple sclerosis is a long term autoimmune disease that can affect the central nervous system(the brain and the spinal cord). Know more about Multiple sclerosis, its causes, symptoms, treatment, links and videos on Health-Wiki | Practo
Anemia is a very common disorder of blood in which your blood has a lower than normal number of red blood cells. Know more about Anemia, its causes, symptoms, definition, treatment and other useful facts, links and videos on Health-Wiki | Practo
Rheumatoid Arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disease. Find more about the treatment, home remedies, reviews and queries on rheumatoid arthritis on Health-Wiki | Practo


