
Contents
In this article we will look at:
- What is diabetes mellitus type 2?
- How does diabetes type 2 occur?
- Who is prone to diabetes type 2 ?
- Symptoms of diabetes type 2
- Diagnosis of diabetes type 2
- Complications of diabetes type 2
- Treatment for diabetes type 2
You can click on any of the links above to navigate to the section of your interest.
What is diabetes mellitus type 2?
Diabetes type 2 is the most common form of diabetes mellitus in the world. Insulin resistance by the body is the regularly observed cause of diabetes type 2.
However, there is also another uncommon factor which causes diabetes type 2, that is, the body simply does not produce enough insulin.
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that allows your body to use glucose (a type of sugar found in many carbohydrates) for energy. Insulin also helps to balance your blood glucose or blood sugar levels, by preventing it from getting too high (hyperglycemia) or too low (hypoglycemia).
Following are the normal and diabetic blood sugar levels:
Plasma Glucose Test | Normal | Pre-Diabetes | Diabetes |
Random | Below 11.1 mmol/l Below 200 mg/dl | N/A | More than 11.1mmol/l More than 200 mg/dl |
Fasting | Below 6.1 mmol/l Below 108 mg/dl | 6.1 to 6.9 mmol/l 108 to 125 mg/dl | More than 7.0 mmol/l More than 126 mg/dl |
2 Hour Post-Prandial | Below 7.8 mmol/l Below 140 mg/dl | 7.8 to 11.0 mmol/l 140 to 199 mg/dl | More than 11.1mmol/l More than 200 mg/dl |
Please Note: If your glucose levels are below 50 mg/dL or above 200 mg/dL you need to be admitted to the emergency room without delay.
How does diabetes type 2 occur?

The primary cause of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 is that the pancreas may produce enough insulin to transport sugar into the cells, however, the body refuses to use the insulin.
Insulin helps to unlock the cells of the body to allow the sugar (glucose) to enter them so that the glucose is transformed into energy.
If there is more sugar in the body than is required, the insulin helps to store the sugar in the liver and releases it when the blood sugar level is low, or when the body needs more sugar, such as in between meals or during vigorous physical activity. Therefore, insulin helps to balance out the blood sugar level and keep it in a normal range. As blood sugar level increases, the pancreas secrete more insulin.
In diabetes type 2 since the body refuses to use the insulin produced, the insulin is unable to let the sugar enter the cells and transform into energy. The sugar level keeps increasing in the blood, and overtime hurts the eyes, heart, kidneys and nerves.
The insulin is not able to let the sugar enter the cells and transform into energy. The sugar keeps increasing in the blood and overtime hurts the eyes, heart, kidneys and nerves.
A secondary reason for diabetes mellitus type 2 is insufficient insulin production by the pancreas. A study done by a team of researchers at the Newcastle University shows that this occurs due to fat accumulation in the pancreas.
When the insulin production is not enough, blood sugar levels rise in the body causing diabetes mellitus type 2.
Don't wait or self medicate.
See a doctor now
Who is prone to diabetes type 2?
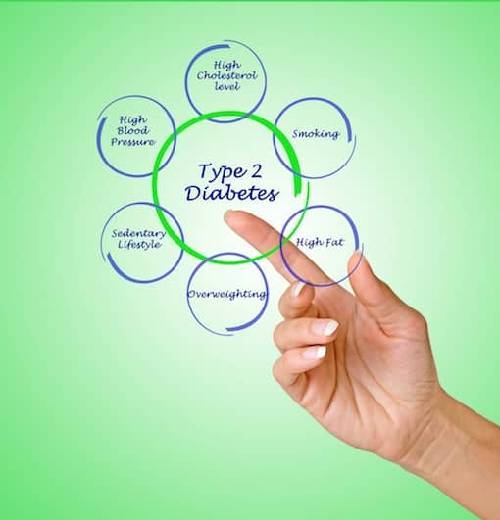

You may be prone to diabetes type 2 if:
- you have a family history of diabetes
- you have prediabetes or a high blood sugar level which has not yet turned to full-fledged diabetes. It can be stopped if you exercise and reduce excess weight
- you lead a sedentary lifestyle
- you have high blood pressure/hypertension
- you have heart disease
- you are overweight
- you are 45 years and above, as with age the risk of getting diabetes grows
- you are a woman with Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
What are the symptoms of diabetes type 2? How is diabetes type 2 diagnosed?
The symptoms of diabetes type 2 include:
- excessive urination
- excessive thirst
- dry mouth
- sudden weight loss
- fatigue
- headaches
- increased hunger
- blurry vision
- slow healing wounds
- loss of consciousness
- Impotency
- itching skin
- slow healing wounds
- frequent yeast infections if you are a woman
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of diabetes type 2 usually includes one or more blood tests.
The doctor will advise you to undergo a Glycated haemoglobin (A1C) test. This test indicates your blood sugar levels for the past two to three months.
This test measures the percentage of haemoglobin — an oxygen-transporting protein in red blood cells — to which the blood sugar is attached. A high percentage of haemoglobin (6.5 % or higher) indicates diabetes.
After this test, the doctor will ask you to undergo an autoantibody test which checks for antibodies that attack the pancreatic cells. This test accurately diagnoses whether it is Diabetes Type 1 or Type 2.
The doctor may also ask you to undergo a Random Blood Sugar Test, a Fasting Blood Sugar Test, and Oral glucose tolerance test.
What are the complications of diabetes type 2?
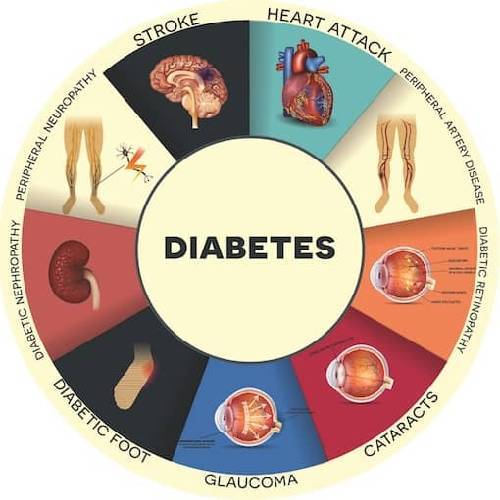
The complications of diabetes type 2 include:
- heart palpitations
- excessive sweating
- slurred speech
- whiteness of skin
- confusion
- headache
- anxiety
- numbness in fingers, toes, and lips
- drowsiness
More severe complications of diabetes type 2 include:
- diabetic retinopathy or eye disorders
- nephropathy or kidney disease
- diabetic neuropathy or nerve disorders
- macrovascular problems or heart problems due to damaged blood vessels
What is the treatment for diabetes type 2?
Medical Treatment
For managing the symptoms of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 the doctor often prescribes a good diet and proper exercise.
Sometimes though, only lifestyle changes are not enough. You may have to undergo treatments which include oral drugs and injectables. Please consult your physician for the appropriate treatment course.
Exercise
If you have diabetes mellitus type 2, you have too much glucose in your blood. Exercising will help you bring your blood glucose levels under control. It helps the muscles to use up the glucose, without the insulin, which brings down the levels of sugar in the blood.
An additional benefit is that the exercising will keep your heart healthy, which is important because people with diabetes are at a high risk of suffering from cardiovascular diseases, due to blocked arteries.
Warning: To avoid any serious risk to your health, please consult your doctor before starting a new exercise regimen. You may need to change your diet, and the dosage of insulin, or of other medicines before you start exercising.
Patient Experiences


Questions answered by trusted doctors




Did you know?
India, the diabetes capital of the world
India holds the record of being the diabetes capital of the world. Over 30 million people have now been diagnosed with diabetes in India. Half of them are women.
Diabetes cases are higher in south india
Cases of diabetes are higher in the four South Indian states of Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh and Kerala.
Children are highly affected too
Around 40000 children under the age of 15 years have been diagnosed with Type 2 Diabetes and this figure is growing by 5% each year. No regular exercise, obesity and a family history of Diabetes are the main causes.
Related videos
Related articles
The treatment method of using various treatments like chemotherapy, radiation, anti-cancer drugs to either cure, treat, control, or reduce the symptoms of any types of cancer can be grouped together as cancer treatments.
AIDS is a set of symptoms caused by the HIV virus. Know more about AIDS, its causes, symptoms, treatment and other useful facts, links and videos on Health-Wiki | Practo
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease which can affect many body parts, including the joints, skin, kidneys, heart, lungs, blood vessels, or brain. Know more about Lupus, its causes, symptoms, treatment and other useful facts, and videos on Health-Wiki




