
Contents
In this article we will look at:
- What is genital herpes?
- How does genital herpes occur?
- What are the symptoms of genital herpes? How is genital herpes diagnosed?
- What are the complications of genital herpes?
- Who is prone to genital herpes?
- What is the treatment of genital herpes?
- In the Spotlight - Latest News on Genital Herpes
- Home remedies for Genital Herpes (end of page)
You can click on any of the links above to navigate to the section of your interest.
What is genital herpes?
A sexually transmitted disease (STD), genital herpes is caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). This virus is generally found in infected people’s saliva, semen, and vaginal secretions.
In men, genital herpes causes blisters or sores on the penis, scrotum, or buttocks (near or around the anus). Women suffer from blisters or sores, around or near the vagina, anus, and buttocks.
It generally produces very mild symptoms, hence many people are not even aware that they have genital herpes.
How does genital herpes occur?
Genital herpes virus spreads through sexual contact. This occurs even if the person carrying the virus does not have symptoms or show signs of infection.
Once the virus enters through the skin, it travels along nerve paths. The first outbreak of genital herpes may appear as early as two days after you have contracted the virus, or even after 30 days.
The virus may also become dormant in the nerves and remain inactive there indefinitely.
In some patients, the virus may become active from time to time. Active viruses travel back along the nerve path to the surface of the skin, where some viruses are shed. When viruses are shed, in some cases there usually is an outbreak of symptoms such as the appearance of sores and blisters, while in others the condition may remain undetected.
In either case, since the virus is active it easily passes from one partner to another during sexual contact. A condom may also not be able to protect the uninfected partner, since the virus may be on a part of the skin which is uncovered.
The herpes simplex virus cannot survive outside the body, therefore, it's nearly impossible to contract the infection through contact with toilets, towels or other objects used by an infected person.
What are the symptoms of genital herpes? How is genital herpes diagnosed?
The common symptoms of genital herpes include:
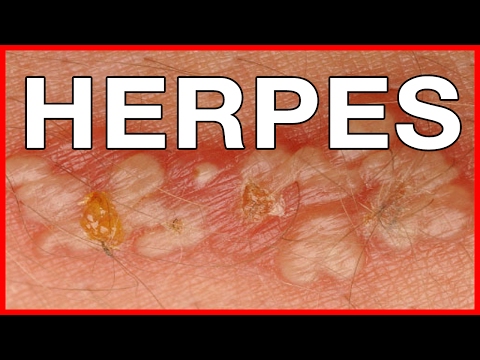
- blisters in the mouth, lips (this is known as herpes labialis), face, vagina, penis, in and around the anus, buttocks and any part of the body that comes into contact with the infected areas
- itchiness or tingling in the infected areas
- blisters can convert to open sores oozing fluid
- crust over the sores
- swollen lymph glands
- headaches
- body aches
- fever
- pain while urinating
- meningitis
- encephalitis
- eczema herpetiform
- eye infection
Diagnosis
An examination of the blisters or sores can reveal to the doctor if it is genital herpes.
He may suggest you to undergo some laboratory tests such as blood tests to confirm the diagnosis, although laboratory tests are not always necessary. Blood tests effectively diagnose herpes simplex virus even before the symptoms appear.

What are the complications of genital herpes?
The common complications that may stem from genital herpes include:
- Encephalitis
- Myelitis
- Lumbosacral radiculitis
- Pneumonitis (lung infection)
- Spread of the virus to other organs
- Incontinence
- AIDS
- Bladder problems
- Rectal inflammation
If you are pregnant and have contracted genital herpes, chances are you will transmit herpes to your baby. Babies who contract genital herpes can suffer from serious complications such as:
- blindness
- brain damage due to herpes meningitis
- chronic herpes skin infection
- death
Who is prone to genital herpes?
People who are prone to genital herpes include:
- people with a history of prior sexually transmitted diseases
- those who are too young of age for first sexual intercourse
- those who have a high number of sexual partners
- those of poor socioeconomic status
- those with compromised immune systems, notably patients with HIV
- patients who have undergone transplants
What is the treatment of genital herpes?
To treat genital herpes your doctor may prescribe some anti-viral drugs. These drugs can reduce the duration and frequency of herpes outbreaks. They can also help reduce the risk of transmission of the virus to a susceptible partner. The treatment plan will depend on your general health condition. If other health complications such as, encephalitis or AIDS develop due to the genital herpes infection, the doctor will prepare a treatment plan for you accordingly.
It is necessary to describe your medical history and symptoms in detail to your doctor, so that he can perform the appropriate tests for the diagnosis.
In the Spotlight - Latest News on Genital Herpes
Questions answered by trusted doctors

Did you know?
Genital herpes affecting more people in India by the year
The annual years of healthy life lost per 100,000 people from genital herpes in India has increased by 2.0% since the 1990s.
Older men affected more
For men, the health burden of genital herpes in India, as measured in years of healthy life lost per 100,000 men, peaks at age 55-59.
Middle aged women affected more
Women are harmed at the highest rate from genital herpes in India at age 45-49.
Related videos
Related articles
HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Know more about HIV, its causes, symptoms, treatment and other useful facts, links and videos on Health-Wiki | Practo
Dialysis is a procedure in which the blood is filtered mechanically without the help of the kidneys. If the kidneys are not functioning properly then Dialysis will take over the function of the failed kidneys.
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. Know more about Pneumonia, its causes, symptoms, treatment and other useful facts and links and videos on Health-Wiki | Practo



It would be better if you consult dermatologist.
Blood tests for STI include
HIV
HBsAg
VDRL
Anti herpes virus antibody titres may be done for you and partner after appropriate examination