Contents
In this article we will look at:
- What is syphilis?
- How does syphilis occur?
- Who is prone to syphilis?
- What are the causes of syphilis?
- What are the symptoms of syphilis?
- How is syphilis diagnosed?
- What are the complications of syphilis?
- What is the treatment for syphilis?
You can click on any of the links above to navigate to the section of your interest.
What is syphilis?
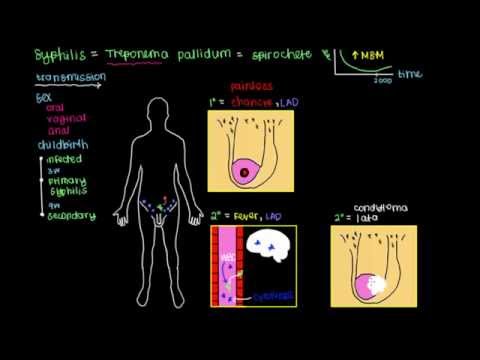
Syphilis is a very common Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD) which can spread through vaginal, anal, or oral sex, though it is commonly spread through oral sex. This is a bacterial infection that can be easily cured with antibiotics in the initial stages. This disease, however, can cause permanent damage such as disability, neurological disorders, and even death if it is left untreated.
How does syphilis occur?
Syphilis occurs if one has sexual intercourse with an infected person.
It is caused by the bacteria called Treponema pallidum (T. pallidum). The bacteria gets transmitted through direct contact with a syphilis sore on the skin. The sores which are painless can start in the vagina, anus, rectum, lips, or mouth. Infact, some people do not even notice the sores since they are painless. The sores usually dry up on their own but the bacteria remains in the body and can remain dormant in the body, for even 30 years before becoming active and damaging internal organs including the brain.
There are four stages of syphilis:
- Primary: This is the stage when the painless sores first appear in the vagina, anus, rectum, lips, or mouth. These sores heal on their own between three to six weeks though at this stage the person can spread syphilis if he/she has sex with someone. At this primary stage, syphilis can easily be cured with antibiotics.
- Secondary: If the disease is not treated at the primary stage it will progress to the secondary stage, which is still curable with medical treatment. The symptoms of secondary stage of syphilis begin to show two to eight weeks after a person becomes infected with primary syphilis. During this stage, a non-itchy rash appears in the body which can be confined to one part of your body, or it can spread to other parts of your body. The rash can be red or reddish brown in appearance and can be smooth or scaly.
The rash can appear to be caused by an entirely different disease which can make the process of diagnosis complicated. In addition to the rash, the person can develop a sore throat, fever, muscle aches, fatigue, wart-like patches around skin folds or genitals,
- Latent: This is the phase when the bacteria lie dormant and no symptoms show up in the body. This phase can last for decades.
- Tertiary: This stage can occur 10 to 30 years after the first onset of the disease. This is the stage when the bacteria wakes up and attacks the internal organs including, heart and brain. This stage can be fatal.
Who is prone to syphilis?
People who are at a high risk of contracting syphilis include:
- those who have unprotected sex
- men who have sex with men
- those suffering from HIV
- people who have numerous sexual partners
- Unborn babies of infected mothers
What are the causes of syphilis?
The main causes of syphilis include:
- direct contact with a syphilis sore on the skin (usually found in the vagina, anus, rectum, in the mouth, or on the lips)
- having vaginal, anal, or oral sex with an infected person
- an infected mother passing syphilis to her unborn child
Syphilis does not spread through casual contacts such as sharing foods, drinks, holding hands, sneezing, sharing towels, coughing, or from toilet seats.
There are chances however of syphilis spreading from prolonged kissing.
What are the symptoms of syphilis? How is syphilis diagnosed?
The symptoms of syphilis change according to the stage of the disease.
Primary stage syphilis symptoms include:
- painless sores first appear in the vagina, anus, rectum, lips, or mouth
- enlarged lymph nodes in the areas of the sore
In the secondary stage the symptoms of syphilis include:
- rough, red, or reddish-brown skin rash, usually on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet, and on the trunk of the body
- oral, anal, and genital wart-like sores
- moist, warty patches (called condylomata lata) in the genitals or skin folds
- fever
- headaches
- general ill feeling
- fatigue
- loss of appetite
- weight loss
- muscle aches
- joint pain
- swollen lymph nodes
- vision changes
- hair loss
In the latent syphilis stage, there are no symptoms. The bacteria lie dormant in this stage for upto 30 years.
The symptoms of tertiary syphilis which can occur 10 to 30 years after the onset of the infection, depends on which organ systems have been affected. The symptoms include:
- damage to the heart, blood vessels, liver, bones, and joints
- soft tissue swellings that occur anywhere on the body
- blindness
- deafness
- mental illness
- memory loss
- destruction of soft tissue and bone
- neurological disorders, such as stroke or meningitis
- heart disease
- neurosyphilis, which is an infection of the brain or spinal cord
Tertiary syphilis is the stage when the disease can become fatal.
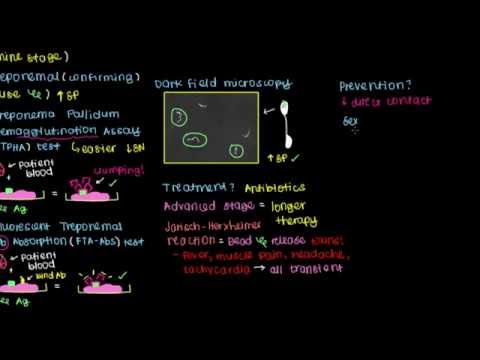
Diagnosis
Usually, a general practitioner or an infectious disease specialist can diagnose syphilis by seeing your symptoms, and conducting tests. Once the diagnosis is complete, depending on the severity and complications of your symptoms, you will be referred to a neurologist or cardiologist for further treatment.
Syphilis can be diagnosed by testing samples of your:
- Blood: through blood tests which can confirm the presence of antibodies that the body produces to fight infection. The antibodies to the bacteria causing syphilis can remain dormant in your body for years. This test can, therefore, reveal past or present infection.
- Cerebrospinal fluid: that is in case the doctor suspects that you have nervous system complications due to syphilis. For this purpose, the doctor will collect your Cerebrospinal fluid through a procedure called lumbar tap.
What are the complications of syphilis?
Some common complications of syphilis, if left untreated during the initial stages, include:
- heart, blood vessel, brain, nervous system damage
- It increases chances of getting HIV and spreading it
- blindness
- deafness
- mental illness
- damage to internal organs
- memory loss
- destruction of soft tissue and bone
- neurological disorders, such as stroke or meningitis
- heart disease
- neurosyphilis, which is an infection of the brain or spinal cord
- death
What is the treatment for syphilis?
Syphilis is easily treatable in its early stages with antibiotics.
Patient Experiences
Questions answered by trusted doctors


Did you know?
Sudden spurt of syphilis cases in India
A once common STD in the pre-antibiotic era, in India, the prevalence of syphilis was brought down from 8% of the population to less than 1% in 2011. However, now almost seven years laters there is a sudden rise in those testing positive for syphilis among other sexually transmitted diseases. There were 1,300 syphilis cases in 2014 which increased to 1,700 the following year. Though doctors say that perhaps it is not a sudden rise but instead cases are coming to the fore due to better awareness and surveillance.
Related videos
Related articles
The treatment method of using various treatments like chemotherapy, radiation, anti-cancer drugs to either cure, treat, control, or reduce the symptoms of any types of cancer can be grouped together as cancer treatments.
Chlamydia is a bacterial infection you can get from sexual contact with another person. Know more about Chlamydia, its causes, symptoms, treatment and other useful facts, links and videos on Health-Wiki | Practo
Gastritis is an inflammation and erosion of the stomach lining, due to bacterial infection, certain pain killers, drinking too much alcohol, very spicy food. Know more about Gastritis, its causes, symptoms, treatment videos on Health-Wiki | Practo.


There is a window period where tests for syphilis can be negative. It is possible that a previous encounter got you infected. Did you at any time have a painless ulcer on your genitals?