
Contents
In this article we will look at:
- What is cholesterol?
- How does cholesterol get distributed in the body?
- How can high cholesterol levels affect you?
- What causes high cholesterol?
- Who is prone to high cholesterol levels?
- What are the symptoms of high cholesterol levels? How is cholesterol diagnosed?
- What are the complications of high cholesterol levels?
- What is the treatment for high cholesterol levels? How to reduce cholesterol?
You can click on any of the links above to navigate to the section of your interest.
What is cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a fat-like substance that is found in every cell of the body. Waxy in texture, cholesterol is essential to produce hormones, vitamin D, and substances that help you digest foods.
Cholesterol is carried through your bloodstream by carriers made of fat (lipid) and proteins called lipoproteins.
Healthy cholesterol levels in the body can protect against heart attack and stroke. However, as the saying goes too much of a good thing is bad, similarly, too much of cholesterol is bad. Too much of cholesterol can lead to a heart attack or stroke.
Cholesterol test
Your cholesterol levels can help your doctor determine the risk you face from a heart attack or stroke. Along with your cholesterol levels, your doctor also checks other factors as well, which include:
- your blood pressure
- whether or not you have diabetes
- your age, sex, and race
- whether or not you smoke
Normal LDL cholesterol levels should be less than 100 mg/dL. A reading of 130 to 159 mg/dL is borderline high and160 to 189 mg/dL is high.
How does cholesterol get distributed in the body?
Cholesterol is carried through your bloodstream by carriers made of fat (lipid) and proteins called lipoproteins.
There are two types of lipoproteins:
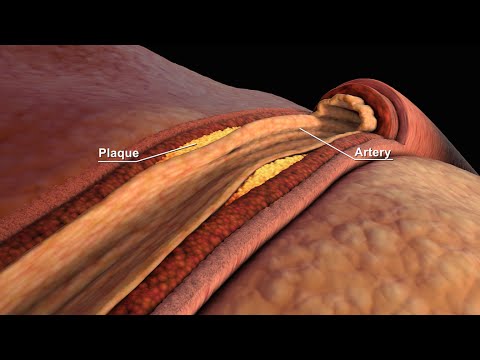
- Low-density lipoprotein (LDL): is the harmful type of cholesterol. If there is too much LDL cholesterol in the blood, it accumulates along the walls of your blood vessels or arteries, forming plaque.
This can raise your chances of a heart attack or stroke. - High-density lipoprotein (HDL): is the beneficial type of cholesterol. HDL helps to remove excess cholesterol from your bloodstream and return it to the liver where it is broken down and passed out of the body.
How can high cholesterol levels affect you?
If there is too much LDL cholesterol in the blood, it accumulates along the walls of your blood vessels or arteries it can slowly build in the arteries and makes them narrower.
As cholesterol deposits accumulate, the arteries harden and grow further narrower. The hardening does not allow them to dilate to the fullest capacity, thus, restricting the blood flow to the heart.
At times the cholesterol deposit or plaque can completely block the arteries, which can result in heart attack or heart failure. The plaque also tends to burst, forming blood clots, which block the blood flow to the heart. This can cause chest pain, also known as angina, or a heart attack.
What causes high cholesterol?
High blood cholesterol is caused by a number of factors which include:
- Poor diet: Consuming saturated fat found in the following food items can raise your cholesterol levels:
- dairy products such as, butter, cream, ghee, regular-fat milk and cheese,
- fatty cuts of beef, pork and lamb, processed meats like salami, sausages and the skin on chicken
- commercially baked cookies and crackers, cream-filled candies
- Obesity: A body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher puts you at an increased risk of high cholesterol.
- Large waist size: The risk of high cholesterol level increases if you are a man with a waist circumference of at least 40 inches or a woman with a waist circumference of at least 35 inches.
- Sedentary lifestyle: Leading a sedentary lifestyle increases the risk of cholesterol formation. Exercising regularly, on the other hand, keeps LDL or the harmful cholesterol in check.
- Smoking: Smoking reduces HDL or the good cholesterol. It injures and even damages the inner lining of the arteries, making it easier for cholesterol and other fats to stick to the blood vessels. This can increase the risk of heart disease, hypertension and stroke.
- Diabetes: Diabetes increases the LDL cholesterol and decreases the HDL cholesterol in the body.It damages the arteries and increases the risk of a heart attack.
Who is prone to high cholesterol levels?
Some people are more prone to high cholesterol levels than others. They include:
- Women who have crossed their menopausal age. Their LDL levels tend to increase after menopause. This increases their risk of heart disease.
- Men above 45 years of age and women over 50 years of age.
- People who have a family history of heart disease.
- People suffering from obesity are at a high risk of suffering from high levels of cholesterol and subsequently, heart diseases.
- People leading sedentary lifestyles.
- People who smoke heavily.
- Women who have a waist circumference of more than 35 inches and men whose waist circumference is more than 45 inches.
What are the symptoms of high cholesterol levels? How is cholesterol diagnosed?
The symptoms of high cholesterol levels include:
- chest pain or angina
- heart attack
- stroke
- pain while walking caused by the blocked arteries that that are unable to send blood to the legs
Diagnosis
A general physician or even a cardiologist can diagnose high cholesterol levels by checking the cholesterol levels in your blood. You may be asked to undergo a blood test called a lipoprotein panel, which can measure your cholesterol levels. Prior to taking the test, you will be asked to fast for around 12 hours to ensure that all food is completely digested and will not affect the results of the test. This test will measure your:
- total cholesterol levels, including LDL or the harmful cholesterol levels and HDL or good cholesterol levels
- triglycerides levels which are a type of fat found in your blood. High levels of triglycerides in the blood may raise the risk of coronary heart disease, especially in women
What are the complications of high cholesterol levels?
High cholesterol levels can cause a number of complications, chief among them being atherosclerosis, which is an accumulation of cholesterol and other substances in the walls of the arteries, forming deposits called plaque. The accumulation of plaque can cause complications such as:
- angina, or chest pain which occurs when blood supply to your heart is affected due to clogged arteries
- heart attack, if the plaque-ridden arteries rupture and blood clots form
- stroke, if the blood flow to the brain is blocked due to clogged arteries
What is the treatment for high cholesterol levels? How to reduce cholesterol?
Medical treatment for high cholesterol
To treat high cholesterol levels your doctor will first suggest lifestyle changes, including diet changes and exercising. If that alone is not sufficient to bring down the high cholesterol levels, he may prescribe medicines to lower your LDL levels. You need to discuss your complete medical history with your doctor before he prescribes medicines to control your cholesterol levels, to ensure that any medicines you are currently taking do not react with the medicines that the doctor would like to prescribe.
Exercise
Exercising regularly can boost up your HDL or good cholesterol levels and burnout dangerous LDL levels.
To reduce cholesterol levels, you can undertake moderate exercising for about 30 minutes daily, or you can undertake vigorous exercise 2 to 3 times per week for 75 minutes.
Brisk walking, swimming, aerobics, bicycling, jogging can reduce your LDL cholesterol levels.
Coupled with exercising you will also need to adopt a healthier diet.
Questions answered by trusted doctors

Did you know?
Heart disease in young people
The likelihood of dying from heart disease in young people doubles with every 40 point increase in total cholesterol.
Low levels of good cholesterol among Indians
72% Indians have low levels of the good cholesterol or HDL holds true across the country, be it in Mumbai, Chandigarh or Chennai.
Boosting good cholesterol
Exercise and taking a good diet are the main methods to boost good cholesterol levels.
Related videos
Related articles
Read about Coronory Artherosclerosis and symptoms, treatments, complications and precautions for it on Health-Wiki | Practo
Breast cancer occurs when healthy cells of breast tissue change and may begin to grow out of control which can appear as a lump within breast tissue. Breast Cancer Treatment includes chemotherapy, radiotherapy,surgery depend on the type of cancer.
Surgical placement of pacemaker in the heart of an individual is called as pacemaker Surgery. This surgery helps to treat slow or irregular heartbeats.


Take more vegetables and polyunsaturated fatty acids like sunflower oil or safflower oil consult dietitian and physician for further evaluation and treatment.